Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, is a common condition that affects the tendons in the shoulder. Specifically, shoulder tendonitis refers to the inflammation of the tendons in the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons that connect the upper arm bone to the shoulder blade. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for shoulder tendonitis.
Common Cause of Shoulder Pain
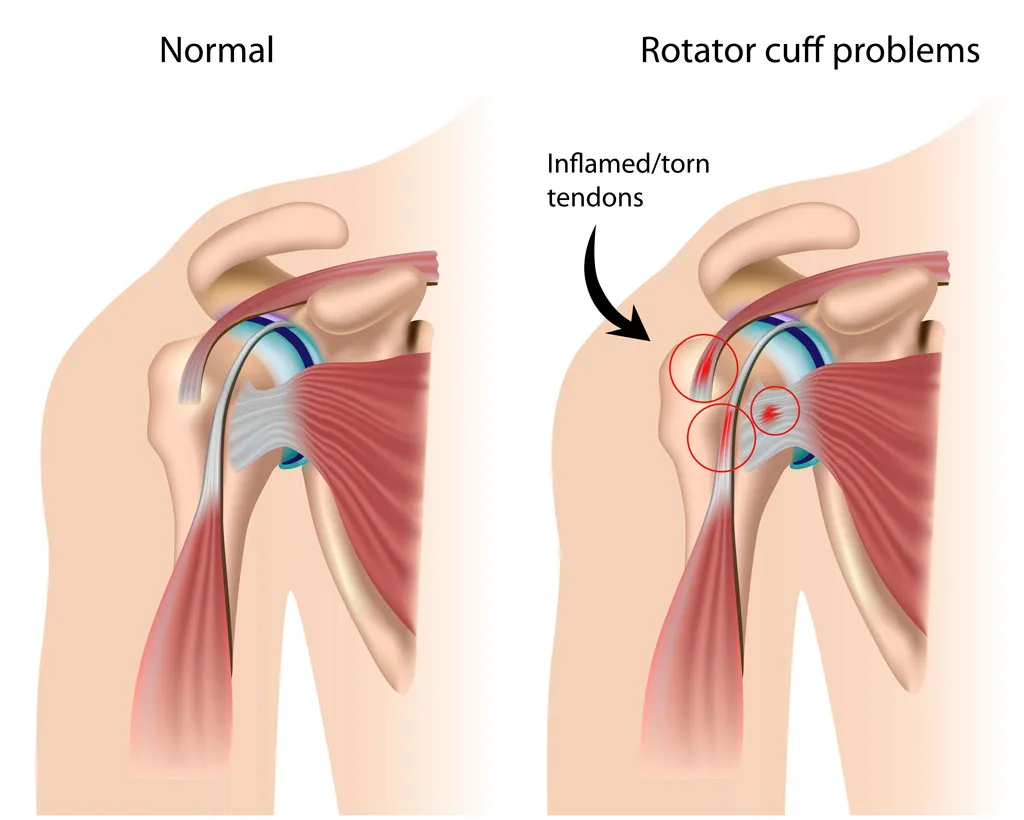
Shoulder tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendons that connect the muscles of the shoulder to the bone. It is usually caused by overuse or repetitive motions, such as those involved in sports or certain jobs that require overhead work or heavy lifting. Here is what you need to know about the causes, treatment, and prevention of shoulder tendinitis:
Causes:
- Overuse or repetitive motions
- Sports that require the arm to move over the head repeatedly, such as baseball, weightlifting, volleyball, racket sports, and certain swimming strokes
- Jobs that require overhead work or heavy lifting
- Direct blow to the shoulder area or falling on an outstretched arm
Treatment:
- Rest: Avoid activities that cause pain, especially if the pain is worse the next day. Avoid the activity that started the problem. Do not use the arm repeatedly out to the side of the body.
- Ice: Apply an ice bag (over a towel) to your shoulder at least twice a day for 20 minutes. Also, apply ice after any activity that aggravates your shoulder pain.
- Medication: An anti-inflammatory pain medication (such as Advil, Aleve, or aspirin) to relieve pain and inflammation. A doctor may recommend an injection of cortisone with lidocaine into the shoulder bursa. If you receive an injection, do not use the shoulder for vigorous activities for about two weeks.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen the shoulder may help prevent a recurrence. Range of motion exercises are also part of the treatment plan.
- Surgery: Surgery may be required to treat shoulder tendinitis and bursitis if it becomes chronic or if there is a tear of the rotator cuff.
Prevention:
- Avoid overuse or repetitive motions
- Use proper technique and form when performing activities that involve the shoulder
- Take frequent breaks during activities that require overhead work or heavy lifting
- Strengthen the muscles of the shoulder through exercise
- Maintain good posture and body mechanics
It is important to note that the information provided is general and may vary depending on individual needs and preferences. It is recommended to consult with a qualified and reputable healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your specific needs.
What is Shoulder Tendonitis?
Shoulder tendonitis occurs when the tendons in the rotator cuff become inflamed. This inflammation can cause pain, stiffness, and difficulty in moving the shoulder. The primary cause of shoulder tendonitis is overuse or repetitive movements, especially those that involve lifting, reaching, or throwing. Other factors that can contribute to the development of shoulder tendonitis include aging, poor posture, and shoulder impingement syndrome.
Causes of Shoulder Tendonitis
Shoulder tendonitis is commonly caused by repetitive activities that put stress on the shoulder tendons. This includes activities such as throwing a baseball, swimming, painting, or lifting heavy objects. Age also plays a role in the development of tendonitis, as the tendons become less flexible and more prone to injury as we get older. Additionally, improper technique or form during physical activities can contribute to the development of shoulder tendonitis.
What Does Tendonitis Feel Like In Shoulder?
The most common symptom of shoulder tendonitis is pain, which is usually felt at the front of the shoulder and can radiate down the arm. This pain may worsen with movement of the shoulder or when lifting objects. Other symptoms of shoulder tendonitis include stiffness, weakness, and a clicking or popping sensation in the shoulder joint.
Here are some common symptoms of shoulder tendinitis:
- Pain and swelling in the front of your shoulder and side of your arm
- Pain triggered by raising or lowering your arm
- A clicking sound when raising your arm
- Stiffness
- Pain that causes you to wake from sleep
- Pain when reaching behind your back
- A loss of mobility and strength in the affected arm
- Minor pain that is present both with activity and at rest
- Pain radiating from the front of the shoulder to the side of the arm
- Sudden pain with lifting and reaching movements
- Pain when arm is at shoulder height or behind back or head
- Shoulder clicking
- Pain when lying on shoulder
- Upper arm pain
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and appropriate treatment plan. Treatment for shoulder tendinitis may include rest, ice, medication, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery. Prevention measures for shoulder tendinitis include avoiding overuse or repetitive motions, using proper technique and form when performing activities that involve the shoulder, taking frequent breaks during activities that require overhead work or heavy lifting, strengthening the muscles of the shoulder through exercise, and maintaining good posture and body mechanics.
Diagnosis of Shoulder Tendonitis
If you are experiencing symptoms of shoulder tendonitis, it is important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. During a physical examination, the doctor will assess your range of motion, check for areas of tenderness, and may order imaging tests such as an X-ray or MRI to rule out other conditions.
Complications of Shoulder Tendonitis
If left untreated, shoulder tendonitis can lead to several complications. The ongoing inflammation and irritation of the tendons can result in further damage to the tissues and may eventually lead to a partial or complete tear of the tendons. This can significantly impact daily activities and sports performance.
Effects on Daily Activities
Shoulder tendonitis can make simple tasks like reaching for objects, lifting, or even combing your hair painful and difficult. The pain and limited range of motion can make it challenging to perform everyday activities, affecting your quality of life.
Potential Long-term Damage
Without appropriate treatment, shoulder tendonitis can cause long-term damage to the rotator cuff tendons. As the condition progresses, the tendons may weaken and become more prone to tears. This can result in chronic pain, loss of strength, and limited mobility in the affected shoulder.
Impact on Sports Performance
Athletes who participate in sports that require repetitive shoulder movements, such as tennis, swimming, or baseball, are at a higher risk of developing shoulder tendonitis. The condition can significantly impact their sports performance and may require them to take a break from their activities to recover.
How is Shoulder Tendonitis Treated?
Treatment for shoulder tendonitis usually involves both non-surgical and surgical options, depending on the severity of the condition. Non-surgical treatment options are typically recommended as the first line of treatment and may include:
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Rest and avoiding activities that worsen the symptoms. Application of ice or heat to reduce inflammation. Physical therapy exercises to improve strength and flexibility. Pain medications or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery may be considered if non-surgical treatments do not provide adequate relief. The surgical options for shoulder tendonitis may include arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure to remove inflamed tissues or repair tears in the tendons, and open surgery, which is necessary in more severe cases to repair or reconstruct the damaged tendons.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
After treatment, rehabilitation and recovery play a crucial role in regaining strength and restoring full function to the shoulder. Physical therapy exercises, stretching, and gradually increasing activity level under the guidance of a healthcare professional are essential for successful recovery.
Preventing Shoulder Tendonitis
Prevention plays a vital role in avoiding shoulder tendonitis. Here are some tips to help prevent the condition:
Proper Warm-up and Stretching Techniques
Before engaging in any physical activity, it is important to warm up the muscles and tendons in the shoulder to prevent strain or injury. Gentle stretching exercises specific to the shoulder can also help improve flexibility.
Strengthening Exercises for the Shoulder
Regular strength training exercises that target the muscles around the shoulder can help improve stability and reduce the risk of tendonitis. This includes exercises such as shoulder presses, rows, and external rotations.
Avoiding Overuse and Repetitive Motions
Try to avoid or limit activities that involve repetitive motions or placing excessive stress on the shoulder. If you must perform such activities, take frequent breaks and ensure proper technique and form.
When to Seek Medical Help
While shoulder pain is common and can often be managed with rest and self-care measures, there are certain signs that indicate the need for medical attention:
Signs of Serious Shoulder Injury
If you experience severe pain, sudden swelling, or deformity in the shoulder joint, it may indicate a more serious shoulder injury such as a dislocation or fracture. Seek immediate medical help in such cases.
Persistent and Worsening Symptoms
If the shoulder pain persists for more than a week or if the symptoms worsen despite rest and self-care, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and treatment.
Difficulty Performing Daily Tasks
If shoulder pain and limited mobility are interfering with your ability to perform basic daily tasks or affecting your quality of life, it is important to seek medical help to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Rotator cuff tendonitis, also known as shoulder tendonitis, is a prevalent condition affecting the tendons that connect your upper arm bone to your shoulder blade. This article has explored the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this ailment. Symptoms may arise from overuse or repetitive movements, often seen in sports or certain occupations involving overhead tasks or heavy lifting. Treatment may include strategies such as rest, icing, medication, physical therapy, and, in severe cases, surgery. To prevent rotator cuff tendonitis, it’s advisable to avoid overuse, maintain proper form, incorporate strengthening exercises, and seek professional advice. For those experiencing persistent or worsening symptoms, seeking timely medical attention is essential to ensure optimal recovery.
Answering your questions about shoulder tendonitis causes
Q: What is shoulder tendonitis?
A: Shoulder tendonitis is an inflammation of the tendons in your shoulder, specifically in the rotator cuff or biceps tendon.
Q: What causes shoulder tendonitis?
A: Shoulder tendonitis is usually caused by repetitive motion or overuse of the shoulder. It can also result from an injury or degeneration of the tendons.
Q: What are the symptoms of shoulder tendonitis?
A: The symptoms of shoulder tendonitis may include pain and discomfort in the shoulder, especially when reaching or lifting, as well as weakness and a decreased range of motion.
Q: How is shoulder tendonitis diagnosed?
A: Shoulder tendonitis is typically diagnosed through a physical examination and a review of your medical history. Additional tests such as X-rays or MRI scans may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Q: What is the treatment for shoulder tendonitis?
A: The treatment for shoulder tendonitis often involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, corticosteroid injections. In severe cases, surgery may be recommended.
Q: What is the rotator cuff?
A: The rotator cuff is a group of tendons and muscles that surround the shoulder joint. It helps to stabilize and move the shoulder.
Q: What is tendinitis?
A: Tendinitis is inflammation of a tendon, which is a thick cord-like structure that connects muscle to bone.
Q: What is rotator cuff tendonitis?
A: Rotator cuff tendonitis, also called rotator cuff tendinitis, is inflammation of the tendons in the rotator cuff.
Q: How is shoulder tendinitis treated?
A: The treatment for shoulder tendinitis is similar to that of shoulder tendonitis and may include rest, physical therapy, medication, and in severe cases, surgery.
Q: How is shoulder impingement related to shoulder tendonitis?
A: Shoulder impingement is a condition in which the tendons of the rotator cuff become compressed or “pinched” between the bones of the shoulder. It is often associated with shoulder tendonitis.

